What is Microcontroller?
 A microcontroller
is a self-contained system with peripherals, memory and a processor
that can be used as an embedded system. Most programmable
microcontrollers that are used today are embedded in other consumer
products or machinery including phones, peripherals, automobiles and
household appliances for computer systems.
A microcontroller
is a self-contained system with peripherals, memory and a processor
that can be used as an embedded system. Most programmable
microcontrollers that are used today are embedded in other consumer
products or machinery including phones, peripherals, automobiles and
household appliances for computer systems.
Due
to that, another name for a microcontroller is "embedded controller."
Some embedded systems are more sophisticated, while others have minimal
requirements for memory and programming length and a low software
complexity. Input and output devices include solenoids, LCD displays,
relays, switches and sensors for data like humidity, temperature or
light level, amongst others.
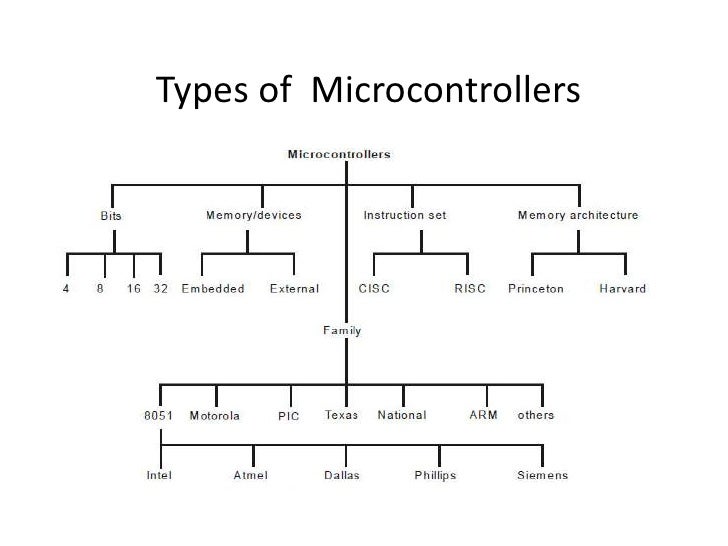
Types of Microcontroller
There are several different kinds of programmable microcontrollers. We can categorized by several parameters including Bits, Flash size, RAM size,instruction set, number of input/output lines, packaging type,architecture, supply voltage and speed.
So let’s discuss;
Bits:
The bits in microcontroller are 8-bits, 16-bits and 32-bits microcontroller.
- 4-bit microcontrollers are small size, minimum pin count and low cost controllers which are widely used for low end applications like LED & LCD display drivers ,portable battery chargers etc.. Their power consumption is also low. The popular 4-bit controllers are Renasa M34501 which is a 20 pin DIP chip with 4kB of ROM,256 Bytes of RAM,2-Counters and 14 I/O Pins. Similarly ATAM862 series from ATMEL.
- 8-bit Microcontrollers are the most popular and widely used microcontrollers .About 55% of all CPU sold in the world are 8-bit microcontrollers only.The 8-bit microcontroller has 8-bitinternal bus and the ALU performs all the arithmetic and logical operations on a byte instruction. The well known 8-bit microcontroller is 8051 which was designed by Intel in the year 1980 for the use in embedded systems. Other 8-bit microcontrollers are Intel 8031/8052 and Motorola MC68HC11 and AVR Microcontrollers, Microchip’s PIC Microcontrollers 12C5XX ,16C5X and 16C505 etc
- When the microcontroller performs 16-bit arithmetic and logical operations at an instruction, the microcontroller is said to be a 16-bit microcontroller.16 bits microcontroller executes with greater accuracy and performance in contrast to 8-bit. These microcontrollers are having increased memory size and speed of operation when compared to 8-bit microcontrollers.These are most suitable for programming in High level languages like C or C++ .They find applications in disk drivers,modems,printers,scanners and servomotor control. Example of 16 bit microcontroller is Intel 8096.
- 32 bits microcontroller is employed mainly in automatically controlled appliances such as office machines, implantable medical appliances, Automotive control, Communication networks,Robotics,Cell phones ,GPRS & PDAs etc..For EX:PIC32,ARM 7,ARM9 ,SHARP LH79520 ,ATMEL 32 (AVR) ,Texas Instrument’s –. TMS320F2802x/2803x etc..are some of the popular 32-bit microcontrollers. It requires 32-bit instructions to carry out any logical or arithmetic function.
Memory:
The memory devices are divided into two types, they are
- External Memory Microcontroller:
- Embedded Memory Microcontroller:
Instruction Set:
- CISC
- RISC
Example for CISC and RICS:
| CISC: | Mov AX, 4 | RISC: | Mov AX, 0 | |
| Mov BX, 2 | Mov BX, 4 | |||
| ADD BX, AX | Mov CX, 2 | |||
| Begin | ADD AX, BX | |||
| Loop | Begin |
Memory Architecture:
Memory architecture of microcontroller are two types, they are namely:
- Harvard Memory Architecture Microcontroller:
- Princeton Memory Architecture Microcontroller:


No comments:
Post a Comment